Renewable energy has numerous advantages, including increased energy security through diversification of energy supply and decreased reliance on imported fuel. Wind, solar, and hydropower energy do not emit greenhouse gases, which helps to reduce air pollution.
While considering the numerous advantages of renewable energy, we must also consider the current constraints. The sun may be shining and the wind may be blowing today, but the next day may be cloudy and calm. The key is continuous availability, and the solution is reliable energy storage via advanced battery technology.
History of Lead
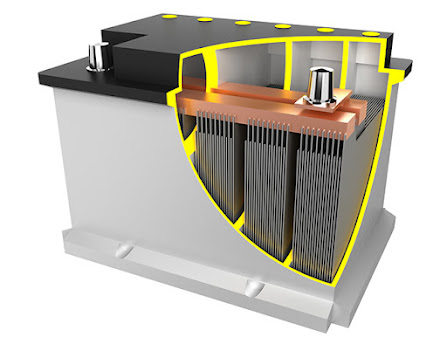
For over 160 years, lead batteries have been in use. Because of their dependability, they have become the most widely used rechargeable battery technology for a wide range of applications. For starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) applications, lead batteries are preferred. Advanced lead batteries, such as Enhanced Flooded Batteries (EFB) and Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM), enable start-stop technology in today's vehicles and supply the extra power needed by advanced safety features and modern conveniences.
Lithium batteries replace gasoline as the vehicle's propulsion source in electric vehicle (EV) applications. Almost every car, however, also has a lead battery to power critical safety functions such as power steering and braking.
In electric vehicle (EV) applications, lithium batteries replace gasoline as the vehicle's propulsion source. However, almost every car also has a lead battery to power critical safety functions like power steering and braking. The lights, entertainment system, and heating/cooling system are also powered by a 12-volt system powered by lead batteries.
Lead batteries are also commonly used as backup power supplies for microgrids, residential solar, telecommunications, utilities, network operation centers, data centers, and even nuclear submarines.
Domestic Manufacturing of Lead
Lead batteries are less expensive to produce than newer battery technologies. According to the Department of Energy, lead batteries have a lower capital cost of Rs 20,300 per kilowatt hour (kWh) than lithium batteries, which have a capital cost of Rs 21,153 per kWh. Lead batteries also use three times less energy to manufacture. Lithium requires 450 kWh per 1 kWh, whereas lead requires 150 kWh per 1 kWh. In other words, the energy used to create a lithium battery is likely to be more expensive due to its energy density. Also, toys battery manufacturer in Indore is the best in their work.
Looking Forward
Major battery manufacturers and suppliers work with researchers to maximize the potential of lead batteries and improve battery performance efficiency. In the last 20 years, battery life has increased by 30 to 35 percent. Lead batteries can last up to 18 years in standby mode, and some have been shown to last up to 30 years. Although it has become very easy to find the best lead acid batteries in Indore.
One current goal is to reduce battery weight while increasing energy density. Lead batteries will become much more competitive with lithium batteries as a result. The Consortium for Battery Innovation is conducting research to increase the cycle life of lead batteries from 1,000 to 5,000, compared to lithium batteries, which have a cycle life of around 2,500 to 4,000.
Conclusion
There are some companies that are mainly focusing on newer technologies as a replacement for lead batteries, we believe that a diverse range of battery technologies is required to ensure that wind, sun, and water power is readily available. Advanced lead batteries are also contributing to the rising demand for energy storage solutions. Lead batteries provide a one-of-a-kind combination of extensive domestic manufacturing infrastructure and unparalleled sustainability.
Comments
Post a Comment